PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
2916.39.0090
SMILES
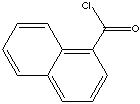
O=C(c1c2c(cccc2)ccc1)Cl
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
1.26 - 1.27
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
Wikipedia Linking:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl_chloride
http://mcat-review.org/
General principles
- relative reactivity of acid derivatives: Acid chloride > Anhydride > Esters > Amides
- Acid halides are the most reactive derivatives because halides are very good leaving groups.
- Amides are the most stable derivatives because NR2- is a terrible leaving group. Also, the C-N bond has a partial double bond characteristic. Proteins are made of peptide bonds, and they are very stable.
- steric effects: bulky groups around the C=O group helps protect the carbon center from nucleophilic attack.
- electronic effects: groups that can redistribute and stabilize negative charges are good leaving groups. For example, the anhydride has a good leaving group - the carboxylate ion - because the COO- can redistribute the negative charge to both oxygens via resonance.
- strain (e.g., beta-lactams)
- Amides have a double bond characteristic between the carbon and nitrogen. This means that the C-N bond can not rotate.
- Normally, the sigma bonds in a ring rotate as to achieve the most stable conformation, but this can't occur for the C-N bond if the ring contains an amide.
- Because of C-N bond in an amide can not rotate, rings that contain amides have higher strain.
- An example of this is the beta-lactam, which is basically a 4 membered ring with 1 amide in it.
Acyl chloride
( A compound consisting of an acyl group bonded
to chlorine.)
Articles referencing this term..............
1-Naphthoyl Chloride is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes and other organic compounds. Building block in the synthesis of MMP inhibitors
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
MELTING POINT
Steel Drum/P.E. Plastic Drum/Plastic Jerry can (UN Approval)